Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
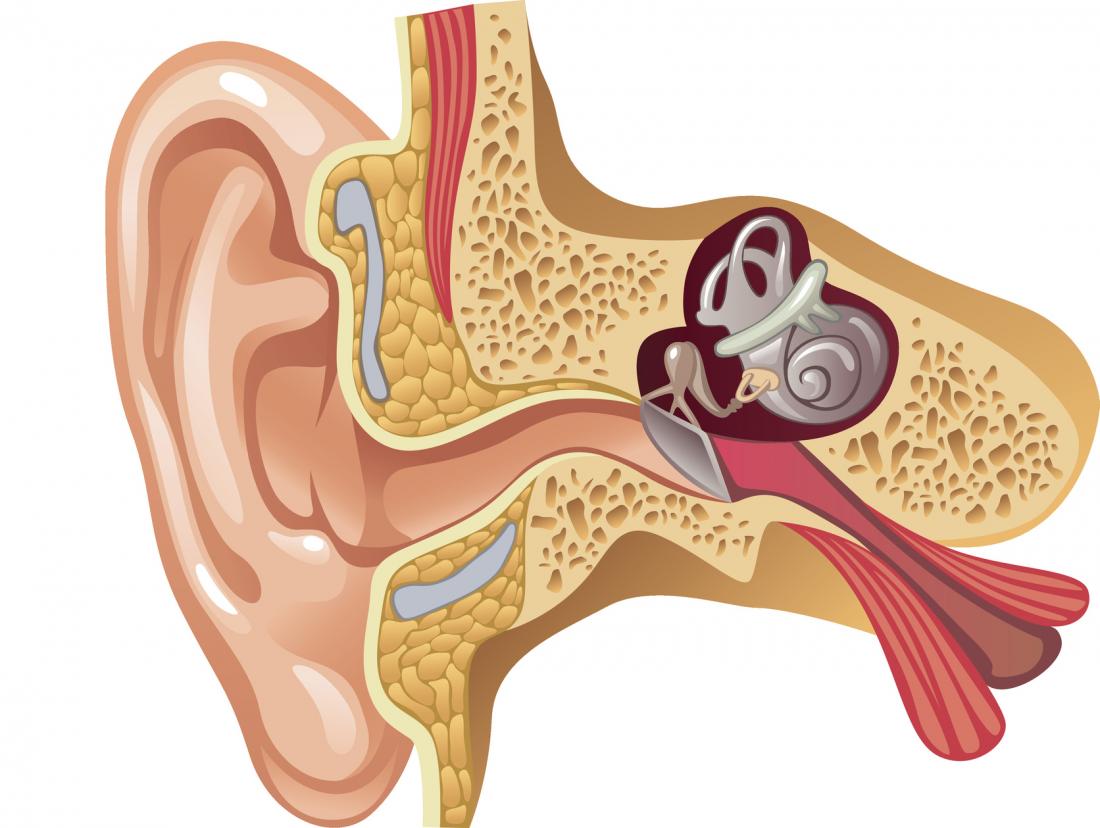
The eustachian tube is a small tube that runs between your middle ear and your throat. It is responsible for draining fluid from your middle ear, and equalizing air pressure. It also protects the middle ear from infections, sounds, and secretions from the back of the nose. It is approx. 3-4 cm long.
The eustachian tube is usually closed and opens when you are chewing, swallowing, or yawning. These actions allow the movement of air into the middle ear and it facilitates the removal of mucus. You can start to have problems when this tube gets blocked or closed. This is called Eustachian Tube Dysfunction.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction include fullness in your ears, blocked ears, tinnitus, pain, and clicking popping sounds or a tickling sensation.
Causes
The common cold is by far the most common cause of eustachian tube dysfunction it often flares up during or after an illness due to inflammation in the mucosal linings. Seasonal allergies are also a culprit, they can create more mucus and therefore congestion. Smoking can damage the small hairs in the middle ear, and obesity can cause small fatty deposits to form around the eustachian tube.
Diagnoses
Diagnoses is usually through taking a health history and examining the ear canal and tympanic membrane.
A small tool called a Pneumatic otoscope is useful for testing the movement of the tympanic membrane in response to pressure changes.
Remedies and Treatment

This condition often self resolves at home in 1-2 weeks however moderate to severe cases may require a trip to your GP or ENT specialist. With treatment it is important to identify the underlying cause and treat that.
Conservative management is focused on trying to naturally open the Eustachian tube. You can try chewing gum, yawning, or the Valsalva manoeuvre.
Medical treatment may consist of a saline nasal spray, antihistamines, oral or topical antibiotics, steroids or a corticosteroid nasal spray.
Surgical treatment is only indicated in severe cases and consists of either making a small spilt in the tympanic membrane to facilitate drainage or implants to help with pressure equalization.